大根堆的定义:
1 大根堆是一个大根树
2 大根堆是一个完全二叉树
所以大根堆用数组表示是连续的,不会出现空白字段。
对于大根堆的插入
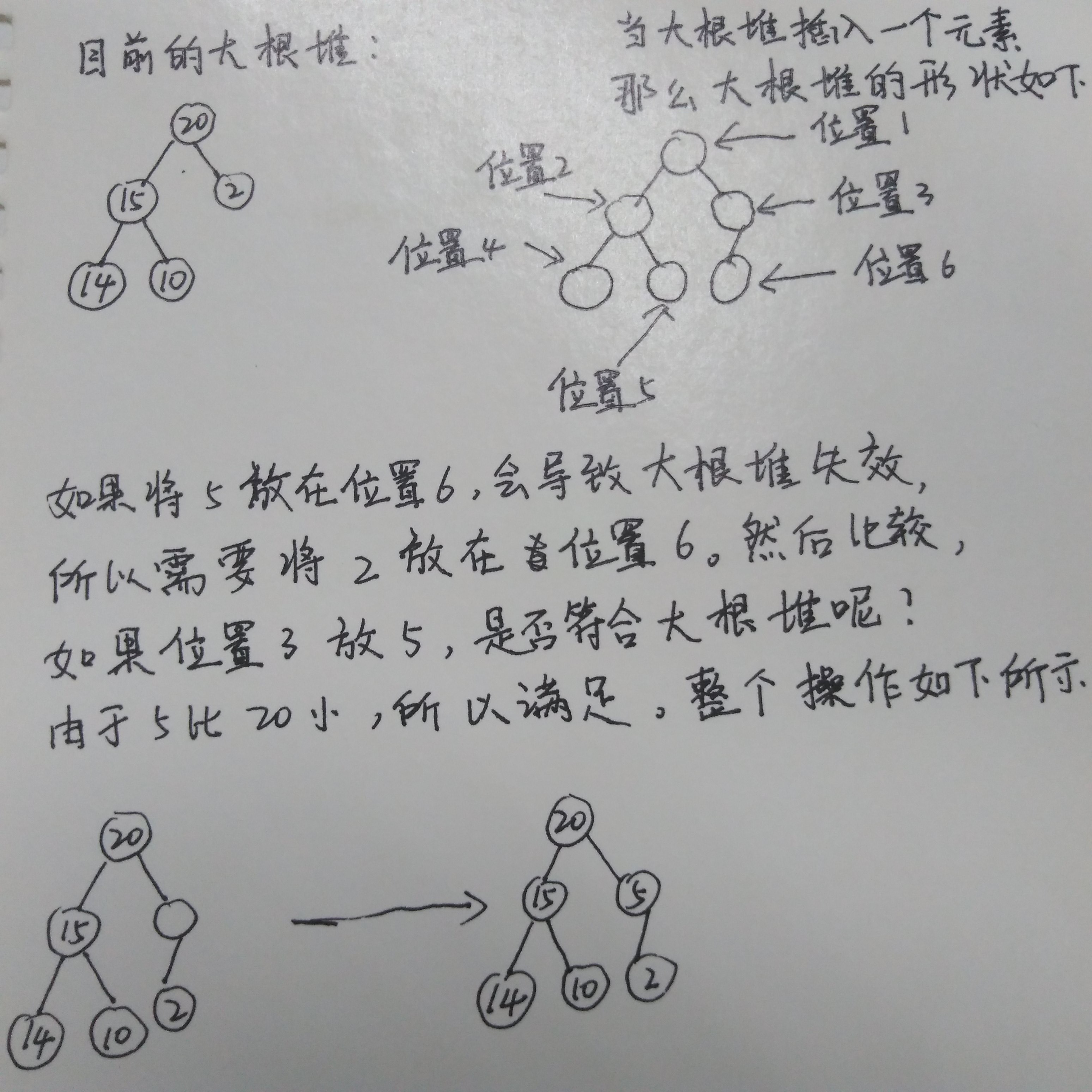
对于大根堆的插入,可以在排序前确定大根堆的形状,可以确定元素5从位置6插入,那么比较元素5和位置3的元素2,
元素5比元素2大,将2下移。接着比较元素5和元素20,一次类推,直到找到元素5的合理位置。
接着看一下如果插入的元素是21,怎么进行排序。
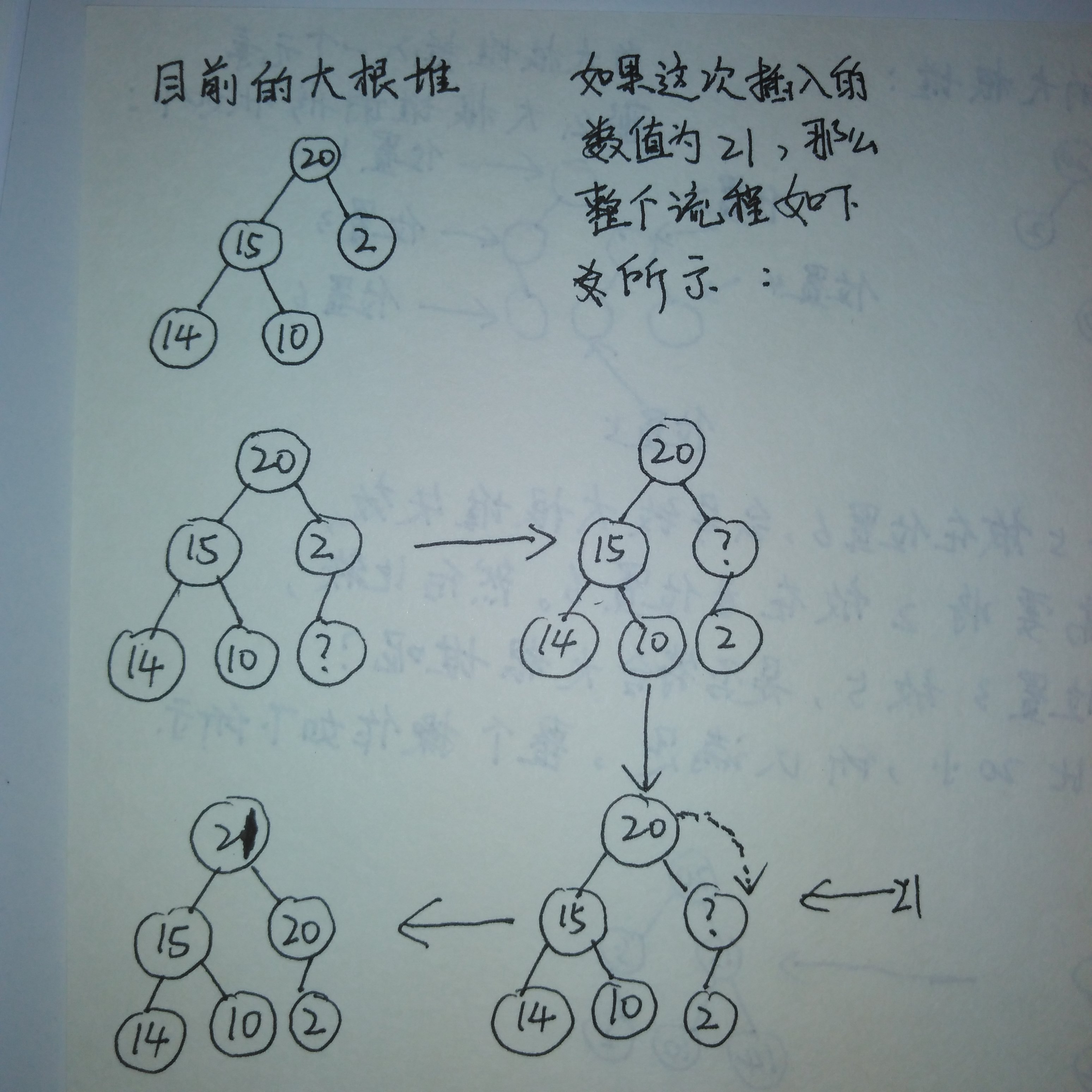
21比2大,所以将2下移,接着比较21和20,发现20比21小,20下移,最终21放到
根的位置。形成大根堆。
对于大根堆的删除
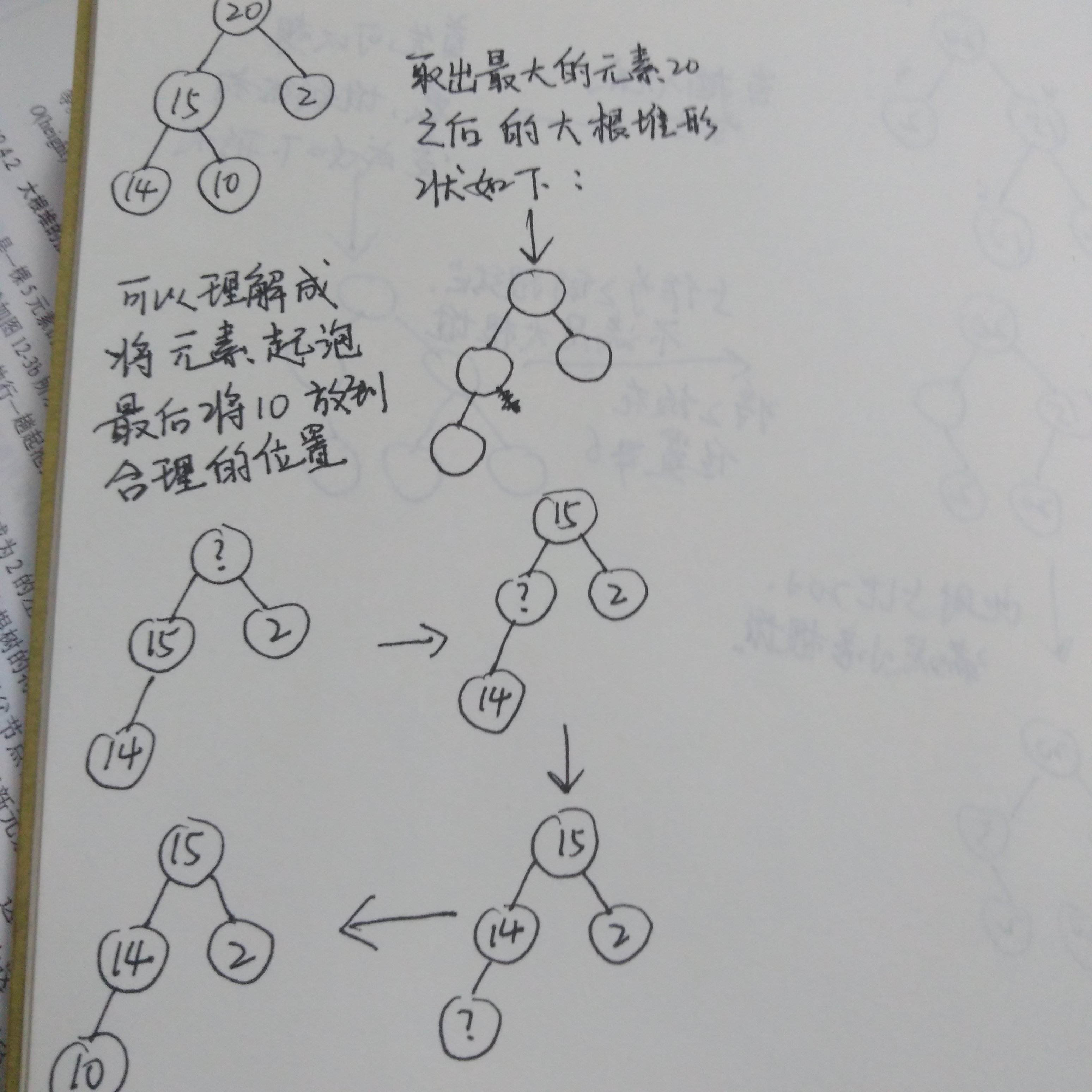
大根堆删除根元素,那么可以确定删除后的形状。可以理解成将最后一个叶子节点放在
合理位置,首先比较叶子节点元素10和根节点的两个孩子15和2,选出两个节点中最大的
元素15,15比10大,所以15进行气泡。放到根节点。然后15所在的位置2,变为不确定的问号。
由于14比10大,那么14起泡放到位置2,根据大根堆的形状,最后将10放到左节点
将一个无序的完全二叉树变为大根堆

将一个无序的完全二叉树变为大根堆(或者小根堆),首先要找到最有一个叶子节点的父节点,
对该父节点为根节点的子树进行排序,生成一个大根堆(小根堆)。然后从节点位置依次
向前做同样的排序,将该节点到根节点的所有子树变为大根堆(小根堆)
举例子:
如上图所示,因为总共有6个节点,6/2 = 3,所以元素19的父节点是位置3的元素4,
将以4位根的子树变为大根堆。因为19比4大,所以19上移,4做叶子节点。依次类推,
从位置3到位置1的所有子树都按照这种逻辑处理,最终变成大根堆。
接着要处理位置2的子树,位置2的元素为1,两个节点为25和12,选最大的元素25,因为
25比1大,所以25进行上移,1变为叶子节点。这样位置2的子树就处理完了。
接着处理位置1,因为位置1的元素为6,两个节点分别为25和19,取最大节点元素25,
因为25比6大,所以25上移,而此时位置2还有两个节点元素1和元素12,需要比较元素6
和这两个节点中最大的,以确定大根堆。由于12比6大,所以12上移,6变为叶子节点。
最终用数组表示这个大根堆就是[25,12,19,1,6,4]
下面是代码实现和测试:
大根堆的类结构:
1 | template <class T> |
两个构造函数:
1 | template <class T> |
插入节点
1 | template <class T> |
打印元素
1 | template <class T> |
pop堆顶的元素,取出最大值
1 | template <class T> |
将一个无序的数组元素,变为大根堆
1 | template <class T> |
源代码下载地址: http://download.csdn.net/detail/secondtonone1/9575112