链表
所谓链表就是一个节点指向另一个节点的数据结构,像一条链子把每个节点连接起来。
如果一个节点既指向了后面的节点,也指向了前面的节点,这些节点就构成了双向链表。
我们先定义这个节点结构
1 | class NodeLRU |
val为节点的数据域表示节点存储的数值
prev为节点的前一个节点
next为节点的后一个节点
然后我们把这些节点串连起来,定义一个链表的结构
一个双向链表的结构图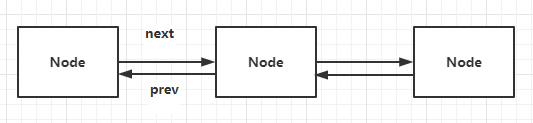
现在我们实现LRU算法:
1 插入一个节点数据域为val,如果链表中有和val匹配的节点,则将该节点移动到链表头,如果没有该节点则直接插入头部。
2 在执行1操作时,如果链表长度已经达到最大,则删除尾节点,在头部插入。
接下来我们实现LRU类,通过插入节点实现LRU算法。
1 | class LRU |
max_size 表示链表最大长度,cur_size表示链表当前长度,head表示链表的头结点,tail表示链表的尾节点。
接下来我们测试LRU类
1 | auto lru = LRU(3); |
程序输出
1 | 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> null |
源码链接https://gitee.com/secondtonone1/algorithms
我的公众号,谢谢关注