信号和槽
当我们需要一个界面通知另一个界面时,可以采用信号和槽机制。通过链接信号和槽,当一个界面发送信号时,链接该信号的槽会被响应,从而达到消息传递的目的。
所以我们先创建一个Qapplication Widgets 应用。Creator会为我们生成mainwindow类和其界面。我们在界面添加一个按钮,按钮的名字叫showChildButton, 按钮显示的文字改为“显示子界面”。
同时为该界面添加一个label,显示的文字修改为“这是主界面”

现在实现点击按钮,在控制台打印一条日志 “show child dialog “
我们先在MainWindow的构造函数中添加信号和槽的链接逻辑
1 | connect(ui->showChildButton, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)), this, SLOT(showChildDialog())); |
然后我们为MainWindow添加showChildDialog槽函数,槽函数需要用slots声明,我们这里在mainwindow.h里用public slots的方式声明槽函数。
1 | public slots: |
接下来去mainwindow.cpp中完成该函数的实现,可以在头文件中右键该函数,在弹出菜单里选择Refactor, 再选择在mainwindow.cpp中添加实现。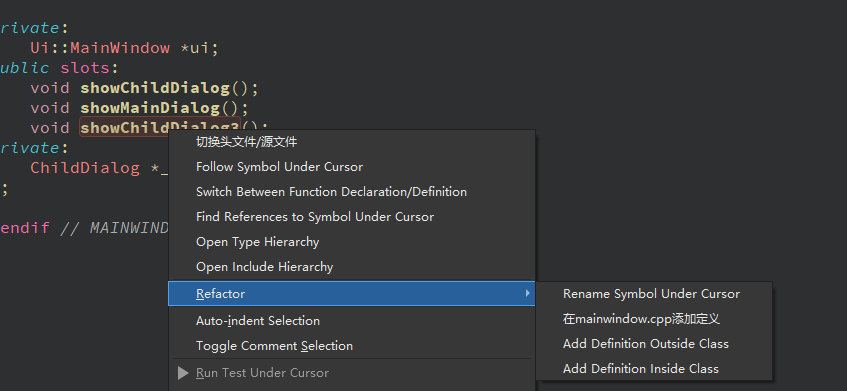
也可以将鼠标光标放置在这个函数上,按alt+enter,弹出菜单选择在mainwindow.cpp中添加实现。这两种方式都是快捷添加,也可以直接去mainwindow.cpp里实现。
1 | void MainWindow::showChildDialog() |
运行项目后点击按钮,就可以看到控制台弹出show child dialog日志。
不同的连接方式
我们上边用来连接信号和槽的方式是qt4提供的方式,用SIGNAL和SLOT将信号和槽转化为字符串。
但是这种方式会存在一定问题,Qt要求槽函数的参数不能超过信号定义的参数,比如我们用到的信号clicked(bool)参数就是bool,我们定义的槽函数showChildDialog()是不带参数的,可以连接成功,如果我们在连接的时候将showChildDialog的参数写为3个,也可以连接成功
1 | //qt4 风格的Slot和Signal 只是宏转换,字符串定义不能检测编译错误 |
但是点击会没有反应,说明qt4 这种连接信号和槽的方式不做编译检查,只是将信号和槽函数转译成字符串。
所以我推荐使用qt5以上版本的连接方式
1 | //推荐qt5 风格 |
这种方式也可以实现信号和槽函数的连接。
实现界面的切换
我们现在实现这样一个demo,程序启动后弹出主界面,点击主界面的按钮弹出子窗口,隐藏主界面,点击子窗口界面的按钮,隐藏子界面,显示主窗口。
所以我们右击项目弹出菜单选择创建Qt设计师界面类,选择Dialog without Buttons,
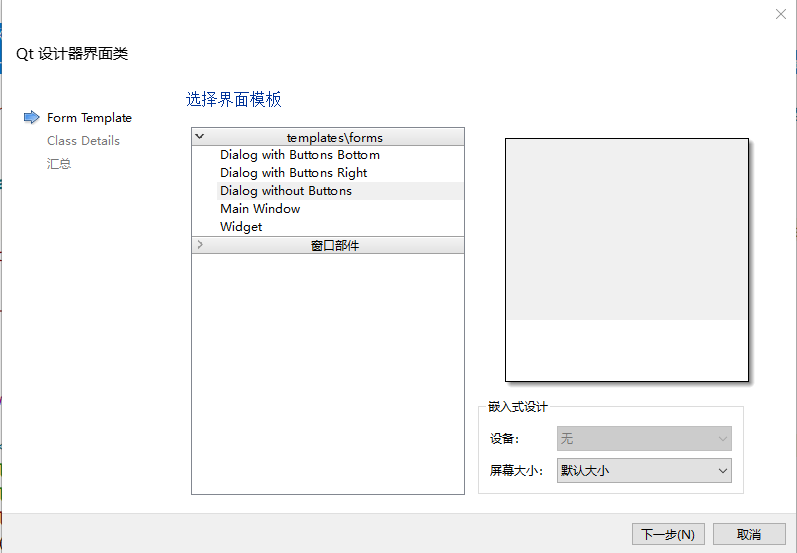
名字选择ChildDialog

我们进入子界面的ui设计界面,添加一个label 描述为这是子界面,添加一个PushButton,文字修改为显示主窗口,并且将按钮的名字修改为showMainWindow
Qt会为我们创建一个界面类名字叫ChildDialog,我们可以将其作为MainWindow类的成员
1 | class MainWindow : public QMainWindow |
然后重新改写槽函数,使点击按钮后弹出对话框
1 | void MainWindow::showChildDialog() |
再次运行程序点击显示子界面的按钮,就会弹出子界面了。关闭子界面,再次点击主窗口的显示子窗口按钮,子窗口又显示出来。
这么做有一个问题就是可能会重复创建子窗口,但是Qt的对象树机制会保证父窗口回收时才回收子窗口,所以关闭子窗口只是隐藏了。
那么随着点击,久而久之窗口会越来越多。
我们想到的一个避免重复创建的办法就是在MainWindow的构造函数里创建好子界面,在槽函数中只控制子界面的显示即可。
但同时要注意在MainWindow的析构函数里回收子界面类对象。
1 | MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : |
这样我们频繁点击显示子界面按钮就不会重复创建窗口了。
那接下来实现点击主界面的按钮,显示子界面,并隐藏主窗口。
实现点击子界面的按钮,显示主窗口,并隐藏子界面。
先实现点击子界面按钮显示主窗口,我们可以在ChildDialog类修改下构造函数,使其接受一个QWidget指针,这个指针指向父窗口也就是MainWindow.
我们新增成员_parent用来存储MainWindow。
新增槽函数showMainWindow用来显示主窗口。
1 | class ChildDialog : public QDialog |
在ChildDialog的实现文件里连接槽函数,并且实现子界面隐藏,主界面显示
1 | ChildDialog::ChildDialog(QWidget *parent) : |
修改主界面的槽函数,让主界面隐藏,子界面显示
1 | void MainWindow::showChildDialog() |
运行程序后,点击按钮就可以实现界面的切换。
这么做有一个不好的地方就是在ChildDialog类里保存了MainWindow的指针,如果我们ChildDialog类里要实现和多个其他界面的交互,就需要保存多个指针,这样代码的耦合性太大了。所以我们引入信号和槽机制,当我们点击子界面按钮时发送一个信号给主界面,这样主界面收到该信号后就显示主界面隐藏子界面。
那我们先为ChildDialog类声明一个信号,用来通知主界面显示
1 | class ChildDialog : public QDialog |
showMainSig是一个信号,用来通知主界面,所以主界面MainWindow类要连接这个信号,我们先在主界面类中声明这个函数
1 | class MainWindow : public QMainWindow |
showMainDialog 是新增的槽函数,用来连接ChildDialog的showMainSig信号。
我们修改ChildDialog的showMainWindow函数
1 | void ChildDialog::showMainWindow() |
然后在MainWindow连接这个信号
1 | MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) : |
再次运行程序,点击按钮实现了界面的切换。
连接信号
上面的程序还可以进一步优化,因为Qt提供了信号连接信号的方式,也就是说我们可以把子界面的按钮点击信号和showMainSig信号连接起来。
1 | ChildDialog::ChildDialog(QWidget *parent) : |
将clicked和showMainSig两个信号连接起来,也可以实现消息的传递,让代码更简洁了。
总结
视频链接视频教程
源码链接https://gitee.com/secondtonone1/qt-learning-notes